Cruise ships
A cruise ship is an ideal and self-sufficient floating city in constant communication with land. It is designed, built and managed to respect the ecosystems of the areas in which it must operate and to safeguard the health and life of those temporarily living there for work or fun, thousands of people from different countries and cultures, who live together and adhere to its rules of governance.
We are committed to develop innovative technologies using the knowledge and skills acquired over the years in order to contribute to the creation of environmentally sustainable products, services and infrastructures. In our strategies, we have embraced the objectives of the International Maritime Organization (IMO), the specialized United Nations Agency protecting the safety of human life at sea and the environment, summarized in the slogan “Safe, secure and efficient shipping on clean oceans.”
Our ships represent a technological benchmark at the European and global level. They feature the most advanced technologies, with technical solutions that provide energy savings, emission reduction, high performance and high quality. In particular, we follow all the international best practices to minimize a ship’s environmental impact throughout its entire life cycle.
We also play an active and proactive role in the development of international safety regulations and we are an accredited representative with the IMO, whose main conventions are aimed at:
- improving maritime security (mostly from a safety point of view) – SOLAS;
- limiting the pollution of the seas – MARPOL;
- standardizing maritime labour rules – ILO.
Our commitments are aligned with the regulatory framework, globally and locally, that mandates rapid progressive reductions in emissions to air and water. In particular, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) has imposed targets to reduce average CO2 intensity per ton/mile from 2008 levels by 40 % by 2030 and to reduce total annual greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by at least 70 % from 2008 levels by 2040.
Both at IMO andat European level, even more challenging targets are being discussed, which, through the application of new technologies and fuels and the revision of the regulatory framework - which introduces the well to wake approach - also aim at the Net Zero concept for cruise ships by 2050. Fincantieri, as stated within the Sustainability Plan 2023-2027, has committed to the same target and the Company is committed and working, subject to technological, regulatory, and infrastructure availability to bring it forward, aiming for 2035.
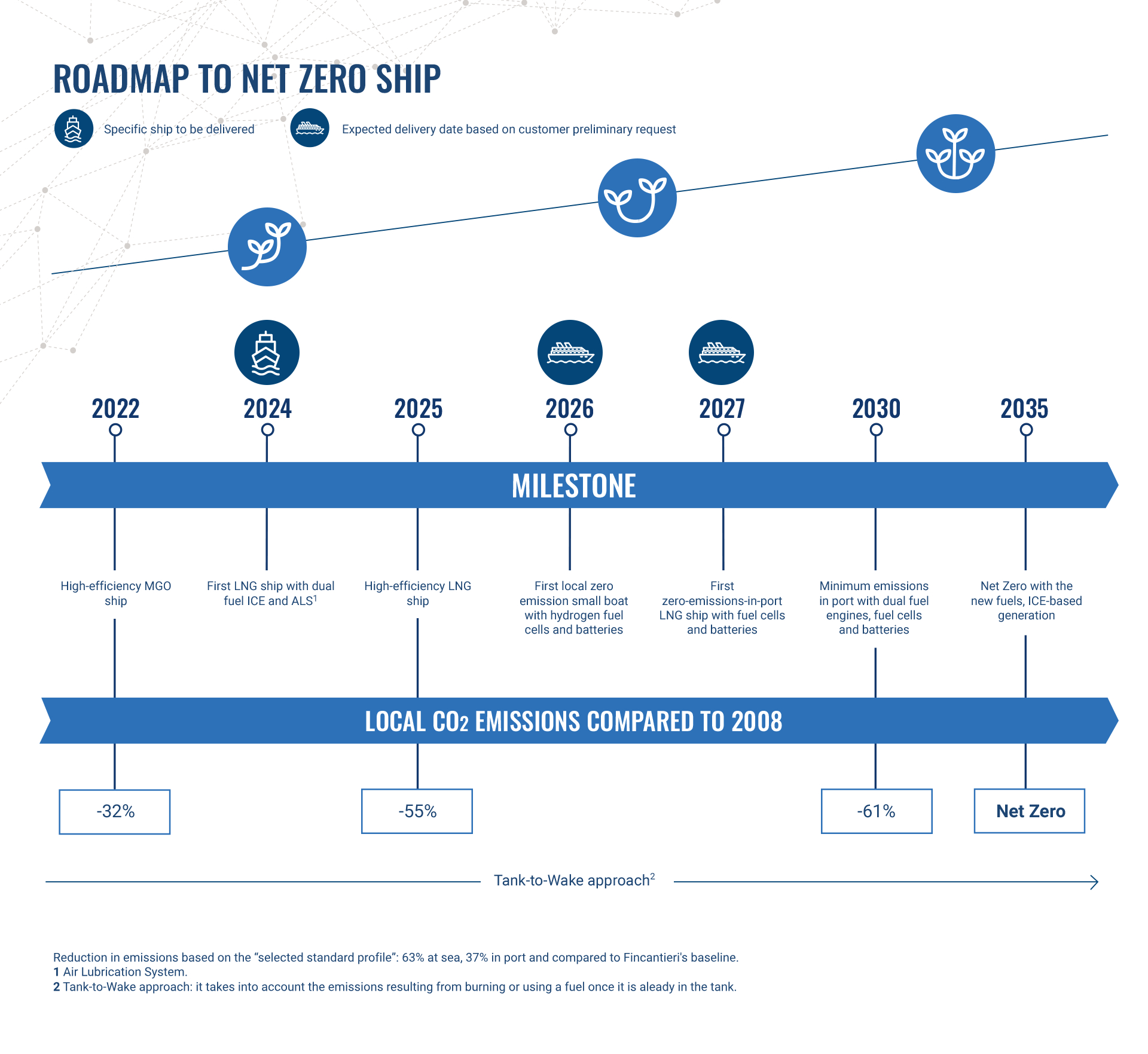

Energy saving and emissions reduction
The reduction of environmental impact has become one of the most important drivers for design and innovation in the field of cruise ships.
We have developed, validated and applied more than 100 initiatives on our ships aimed at:
- improving hydrodynamic and propulsive efficiency;
- exploiting waste heat (fumes and cooling water) with recovery and cogeneration systems;
- systematically reducing the energy needs of users on board.
In particular, we have validated and applied on our ships a series of initiatives, included in the Company’s “Ecosustainable Design” procedure, that are also aimed at energy saving and reducing air pollution.
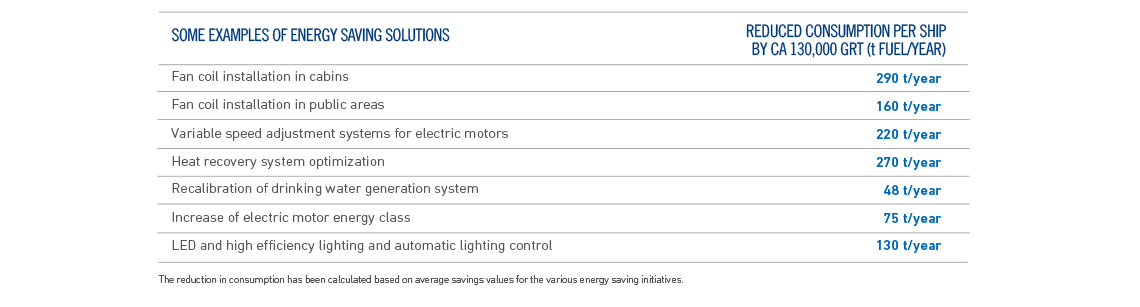

To meet the challenge of reducing emissions, Fincantieri is experimenting with various green technologies, which are described below.
LIQUEFIED NATURAL GAS
The currently most common configuration for emissions reduction is based on latest generation diesel engines combined with the installation of fume purification systems in the exhaust systems. Another method which is gradually being established is the substitution of traditional fuels with Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) in view of the indisputable benefits in terms of emission impact. This reduction is around 25% in terms of CO2 emissions and over 75% in terms of emissions of other particulates.
In recent years, orders for ships with low environmental impact have accelerated, particularly those for dual-fuel ships with LNG primary propulsion. In the past, Fincantieri had already built a special ferry with LNG propulsion for Canada and, in early 2024, delivered a 178,000 GRT cruise ship with LNG as primary fuel, the largest such unit ever produced in Italy.
Fuel cell
The future lies in the application of fuel cells, electrochemical conversion devices that generate electricity and heat by combining a fuel (typically hydrogen, methanol or methane) and a comburent (oxygen), in the absence of combustion. In this way, no polluting substances are actually produced.
The Company has set up a research laboratory, in collaboration with the University of Trieste, with the aim of testing power generation systems based on different types of fuel cells.
METHANOL
Fincantieri is developing plans for new ships with provision for future use of bio or synthetic methanol, which would go into a dual fuel (methanol/MGO) internal combustion engine.
Green methanol, in the well-to-wake scenario, is a promising fuel for achieving the net zero target. The management of methanol on board a ship would be easier than LNG, not requiring cryogenic technology for storage and use.
AMMMONIA AND HYDROGEN
Ammonia and hydrogen are substances that, because they contain no carbon, do not emit CO2 during the combustion process; from this point of view, they are suitable fuels for use in limited areas to pay locally for the goal of zero emissions.
These two fuels, if produced in a green way, in the well-to-wake approach are also both promising for achieving the Net Zero target globally.
In collaboration with the Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (CNR, National Research Council) and the Universities of Genoa, Naples and Palermo, with the contribution of the Italian Ministry of Economic Development, we have developed a project to realize a laboratory ship approximately 25 metres long to study power generation technologies with low environmental impact. The ship, called Zeus – Zero Emission Ultimate Ship, inaugurated at the beginning of 2022, is powered by electric propulsion engines, which will be powered by a fuel cell system of about 130 kW and a battery system capable of ensuring around 6 hours’ navigation autonomy at zero emissions, thanks to about 50 kg of hydrogen contained in metal hydride cylinders. Zeus will be the first marine vessel powered exclusively by fuel cells.
Fincantieri has joined the public-private partnership launched by the European Commission and the Waterborne Technology Platform to decarbonize waterborne transport. The aim is to present zero-emission solutions for all types of ships and services in the maritime segment by 2030, making waterborne transport completely emission-free by 2050. The project is funded by the Horizon Europe research and innovation programme.
Furthermore, Fincantieri is among the 35 European companies participating in the first IPCEI (Important Project of Common European Interest) on hydrogen, which, in July 2022, obtained the European Commission’s authorization for funding through the State Aid scheme envisaged for IPCEIs.
In this area, Fincantieri is investigating possible applications or arrangements for installation of hydrogen-fueled fuel cells.
Ammonia, on the other hand, while a fuel that could ensure that targets are met, does not yet appear to be a possible solution for the cruise market due to its toxicity. However, Fincantieri is initiating research projects to assess the conditions for the applicability of this fuel to the cruise industry.
In order for the targets to be truly achieved, it is essential to both accelerate the development of regulations to regulate the installation and management of innovative fuels, and to promote the increase of sustainable large-scale, along with the development of the necessary infrastructure
Lithium batteries
Another technology we are investing in is lithium batteries. In 2021, we formed the Power4Future joint venture with Faist to focus on this project. As well as powering ships covering short distances, the batteries will also be able to contribute to zero emissions in port when there is no cold ironing.
Fincantieri experimented with this a few years ago, installing a system of mega lithium batteries to power the Grimaldi group’s ferries, thus avoiding the need to run diesel generators during port stopovers.
VARD has delivered various small/medium-sized vessels equipped with electric batteries to cover all or part of the energy requirements and it is committed to testing other innovative solutions.
Cold ironing
One of our goals is to achieve zero emissions in ports by 2030. The solution is cold ironing, the dock electrification system that allows electricity to be supplied to the ship directly from the shore, so that the ship’s engines can be shut down while it is berthed. In addition to reducing polluting emissions, the supply of energy from the grid would help reduce noise pollution and improve comfort on board while in port.
To protect the areas subject to cruise navigation, only bacteriologically and chemically pure water can be discharged into the sea. Any other residue must be stored on board and unloaded in port for further treatment.
In particular, our focus on solid waste treatment is realized using collection, dehumidification, kitchen waste treatment; sorting and recycling of hotel waste; compaction and/or incineration (where permitted) of solid waste; pelletizing, storage of waste for subsequent unloading in port.
Liquid waste initiatives instead concern physical and biological treatment (in line with the best land standards) of all on-board wastewater (sewage, grey water, galley and laundry effluents); storage of purified water; thickening and drying of residual sludge for subsequent unloading in port.
To avoid contamination with species from different ecosystems, we sterilize ballast water before discharging it, using latest generation ballast water treatment systems, based on the pre-filtering of plankton and subsequent sterilization with ultraviolet rays.
Naval vessels
The naval vessel market is strongly influenced by the continual demand to increase efficiency standards in the international defence segment and is one of the most demanding challenges. We are a reference player for many Navies and we face challenges thanks to our consolidated experience in the design sector; our wealth of knowhow has enabled us to deliver over 100 naval vessels since 1990.
A consolidated experience has enabled us to combine the development of platforms with high operational performance with the application of solutions aimed at containing environmental impacts.
The new vessels, some of which are already in service, feature design choices aimed at containing environmental impact in terms of emissions to air, fuel consumption, wastewater treatment, use of special treatments to preserve the hull and the possibility, for certain vessels to be delivered shortly, to contain an area of sea that is polluted, with the possibility of collecting and storing the pollutants on board.
As regards power generation, building on more than ten years of experience of submarines, studies are underway for the use of fuel cells on naval vessels.
In particular, we are focusing on solutions aimed at:
Energy saving and reduction of emissions
The topic is addressed by introducing energy savings criteria developed mainly in ship architecture by selecting endothermic engines (both propulsion engines and power generation engines) with appropriate technological solutions and by selecting high energy efficiency materials or materials with high efficiency heat transfer.


On the other hand, the special characteristics of naval vessels and the consequent system solutions optimized to deliver mission performance do not, currently, enable the introduction of energy recovery systems.
Treatment and storage of solid and liquid waste
The technological solutions adopted for the treatment of solid waste are entrusted to the converters. These machines enable solid waste to be dried and sterilized. The reduction in volume and weight and subsequent automatic vacuum storage allow on-board retention to be increased. The modern converters adopted enable a volume reduction of 70% and weight reduction of 30%.
For liquid waste, we have adopted technological solutions that are in line with the international regulations already used for merchant vessels:
- IMO MEPC 227 (62) for grey water and sewage treatment;
- IMO MEPC 107 (49) for bilge water treatment.
Grey water and sewage are collected into appropriate physical and chemical treatment units which macerate the suspended solids and reduce the contents of the Total Suspended Solids (TSS), Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) and Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) using aerobic processes. The process also envisages disinfection using UV systems.
Which objectives do we have on this topic?
Innovation, Research and Development: 2023-2027 Sustainability Plan objectives and targets
Investments in research and innovation with the aim of developing sustainable, efficient, safe and competitive products and processes with particular reference to the technologies needed to reduce environmental impact and increase their digitalization
Discover the objectives
Research & Innovation Policy
| Description/Target | Timeline | Perimeter | Status | SDGs |
|
Drafting of a Policy that identifies the principles and strategy chosen by the Group to approach product and process research and innovation |
2023 |
Group |
In line with the corporate strategy and objectives, we drafted the Innovation Policy in 2023 to guide the Group’s actions and maintain its leadership in technological innovation in the sectors in which Fincantieri operates. |
|
Development of smart ships and smart offshore infrastructure and autonomous ships. Development of innovative solutions for shipyards (smart yards)
| Description/Target | Timeline | Perimeter | Status | SDGs |
|
• Reference framework for secure interconnection (from a cyber security perspective) of all on-board systems for the exchange/recording of real time data in open formats |
2030 |
Group |
|
|
Environmental Impact of Products and Services: 2023-2027 Sustainability Plan objectives and targets
Development of ecologically sustainable products and services with the aim of contributing to a circular and low carbon economy
Discover the objectives
Developing high energy-efficient cruise ships powered by eco-friendly/ renewable sources, with reduced environmental impact in terms of atmospheric emissions, discharges at sea and noise (green ships)
| Description/Target | Timeline | Perimeter | Status | SDGs |
|
International Maritime Organization (IMO) target for 2025 (30% reduction in cruise ship EEDI* index compared to IMO baseline ref. EEDI-2008**), corresponding to a 30% reduction in CO2 emissions for the same tonnage and miles travelled at the EEDI index baseline speed
* Energy Efficiency Design Index defined by the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL) |
2025 |
Fincantieri S.p.A. |
|
|
|
IMO target for 2030 (40% reduction in cruise ship EEDI index compared to IMO baseline ref. EEDI-2008), corresponding to a 40% reduction in CO2 emissions for the same tonnage and miles travelled at the EEDI index baseline speed and zero emissions in port |
2030 |
|||
|
Net Zero cruise vessels target |
2050 |



